If you’ve ever conversed with an online support bot or used Siri, you’ve encountered chatbots and conversational AI. But what exactly sets a simple chatbot apart from more advanced conversational AI? Business leaders want to know which AI tools are best for their business.
Improve customer and employee experiences.
These technologies are no longer novelties. In fact, a recent Gartner report found that 54% of organizations are already using some form of chatbot, virtual assistant, or other conversational AI in customer-facing applications. And adoption is only growing.
In this article, I’ll break down what each term means, provide real-world examples (from e-commerce to healthcare), and help you figure out when to use a chatbot or a conversational AI solution. I’ll keep things conversational and sprinkle in some firsthand insights (and a bit of humour) to keep it fun.
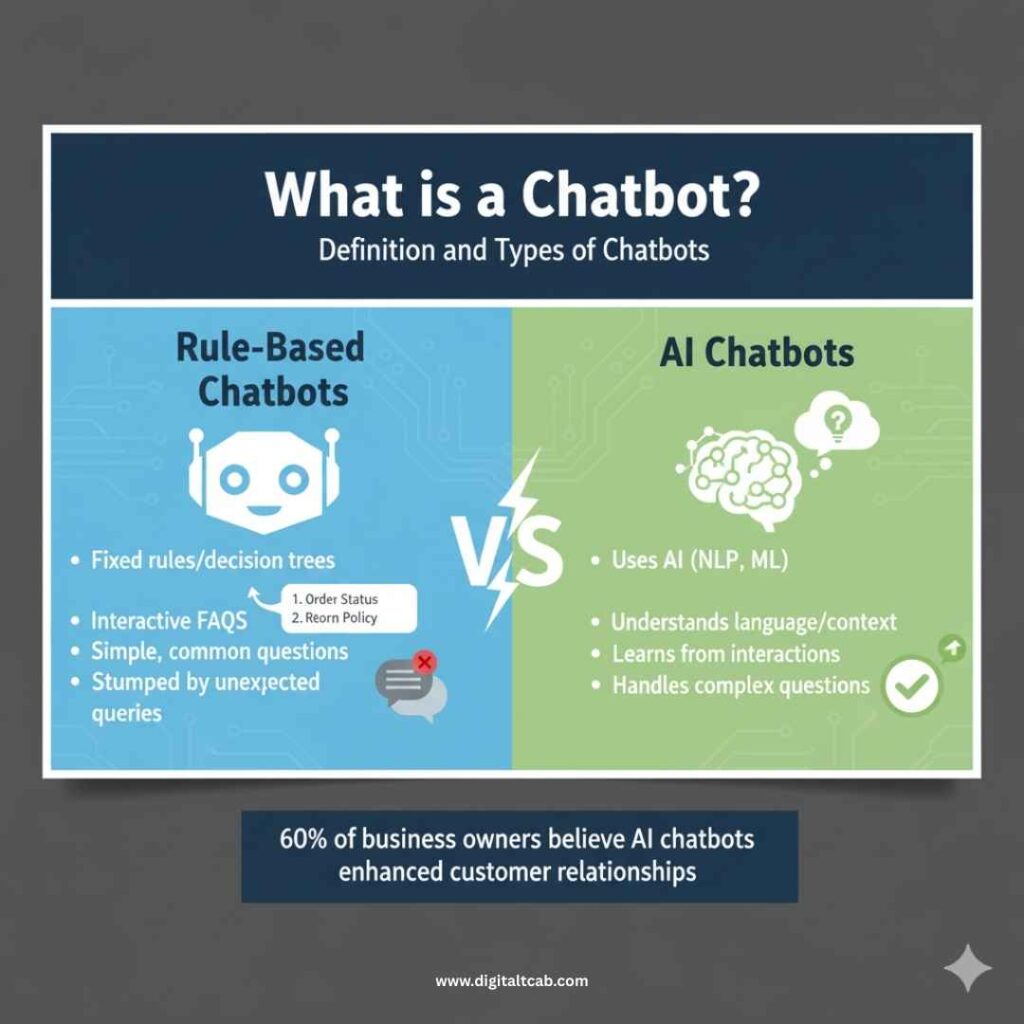
What is a Chatbot? Definition and Types of Chatbots
A chatbot is an AI-powered tool designed to simulate human interactions, enabling users to retrieve information or complete specific tasks. Usually accessible through messaging platforms or embedded chat widgets on websites, chatbots respond to inquiries or provide assistance by following predefined instructions or algorithms.
You encounter chatbots on websites, mobile apps, and social media messengers, wherever instant answers are needed.
I often describe chatbots as automated customer service reps. They follow rules or scripts set by developers. If you’ve used a site’s live chat and gotten quick, menu-based answers (“Please select: Order Status, Store Hours, Return Policy…”), that was likely a rule-based chatbot at work. These basic bots respond to specific keywords or buttons. They cannot truly understand language beyond their programmed rules – if you go off-script, you’ll probably get an “I’m sorry, I didn’t get that” message. (When someone complains that a chatbot was “dumb” or unhelpful, it’s usually because it was a limited rule-based bot without any AI.)
AI chatbots frequently utilize technologies such as Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Machine Learning.
These more advanced bots can interpret what you type (or say), understand your intent, and generate relevant answers. For example, an AI chatbot knows that “I need help resetting my password” is similar to “forgot my login.” Unlike their rule-based cousins, AI chatbots can improve with experience – they learn from each conversation and get better at delivering helpful responses. Notably, approximately 60% of business owners believe that AI-powered chatbots have enhanced customer relationships for their businesses.
Types of Chatbots:
In summary, chatbots generally come in two flavours:
- Rule-Based Chatbots: Operate on fixed rules or decision trees. They’re like interactive FAQs: great for simple, common questions, but they can easily be stumped by anything unexpected.
- AI Chatbots: Use artificial intelligence (NLP, ML) to understand language and context. They continuously learn from interactions, so they handle complex or off-script questions much better over time.
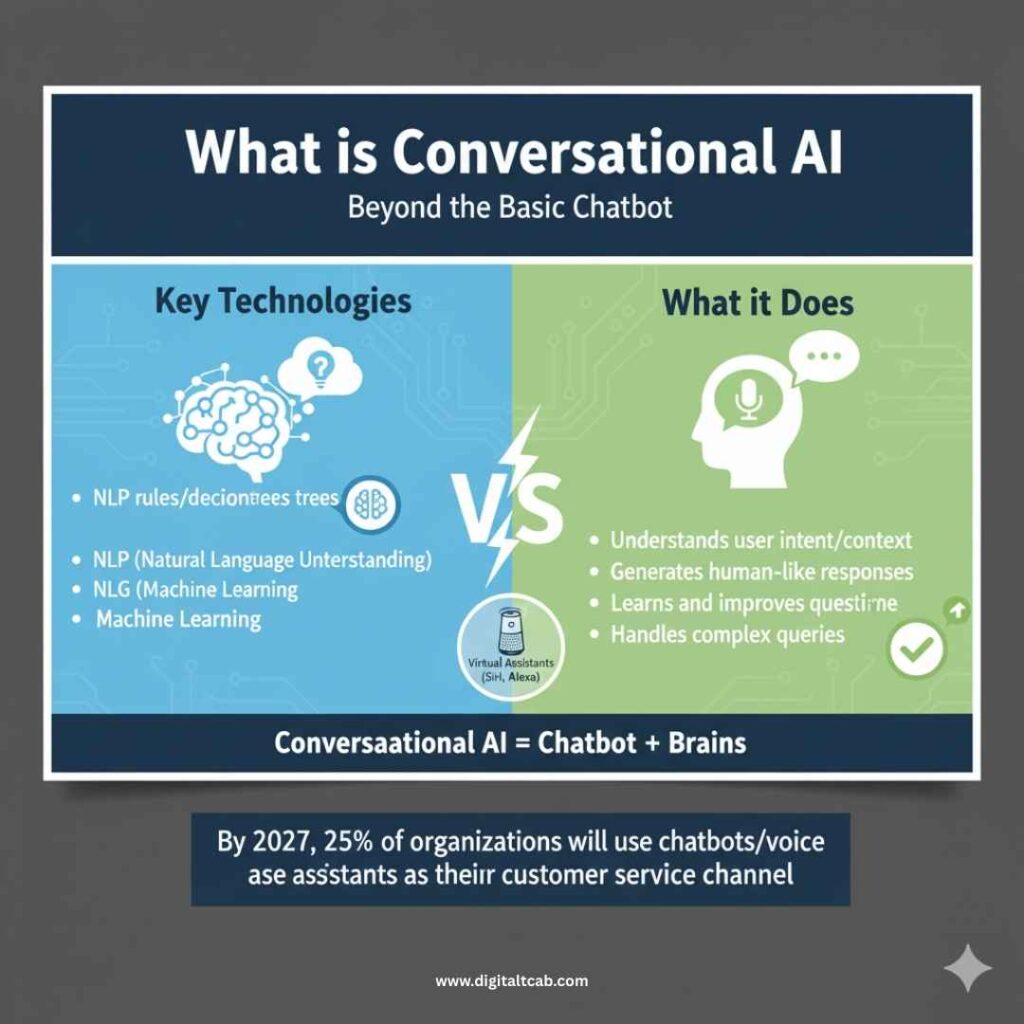
What is Conversational AI? Overview and Components
Conversational AI is a set of technologies that enables computers to have natural, human-like conversations with people.
It includes chatbots, virtual assistants, and any AI-driven system that people can interact with naturally through conversation or messaging. When we discuss conversational AI, we refer to a combination of advanced technologies working together: NLP to understand words, NLU to comprehend intent, NLG to generate responses, and machine learning to improve over time.
At its core, conversational AI uses multiple AI components (language processing, understanding, generation, and continual learning) to make the magic happen. In practical terms, this allows conversational AI to…
Interpret what you ask, even if you phrase it in various ways, and generate a response that feels natural rather than simply reciting a canned line. Recent advances in large language models (think ChatGPT) are pushing conversational AI even further, making bots sound and respond more like real people.
A classic example of conversational AI in action is virtual assistants like Apple’s Siri, Amazon’s Alexa, or Google Assistant. These systems can handle spoken language, understand context (“Set a reminder for next Tuesday at 9 AM”), and even pull in external data (such as your calendar or the weather) to provide helpful answers. Conversational AI isn’t limited to voice; it also powers text-based chatbots on websites and messaging apps. (By 2027, experts predict chatbots and voice assistants will be even more widespread – for roughly 25% of organizations, they’ll be the primary customer service channel.)
Put, conversational AI = chatbot + brains. It enhances the basic chat interface of a bot, making it more intelligent and user-friendly. For example, a conversational AI bot on an airline’s website can understand nuanced questions, such as “Do I need a visa for Japan if I have a Canadian passport?” and provide a relevant answer by accessing contextual data – something a simple FAQ bot cannot do easily.
Conversational AI systems can recognize a user’s intent and context, then respond in a natural, human-like way. This ability to actually “converse” sets them apart from regular chatbots.
For a more detailed breakdown of how conversational AI works (NLP, NLU, etc.), feel free to check out our comprehensive conversational AI guide.
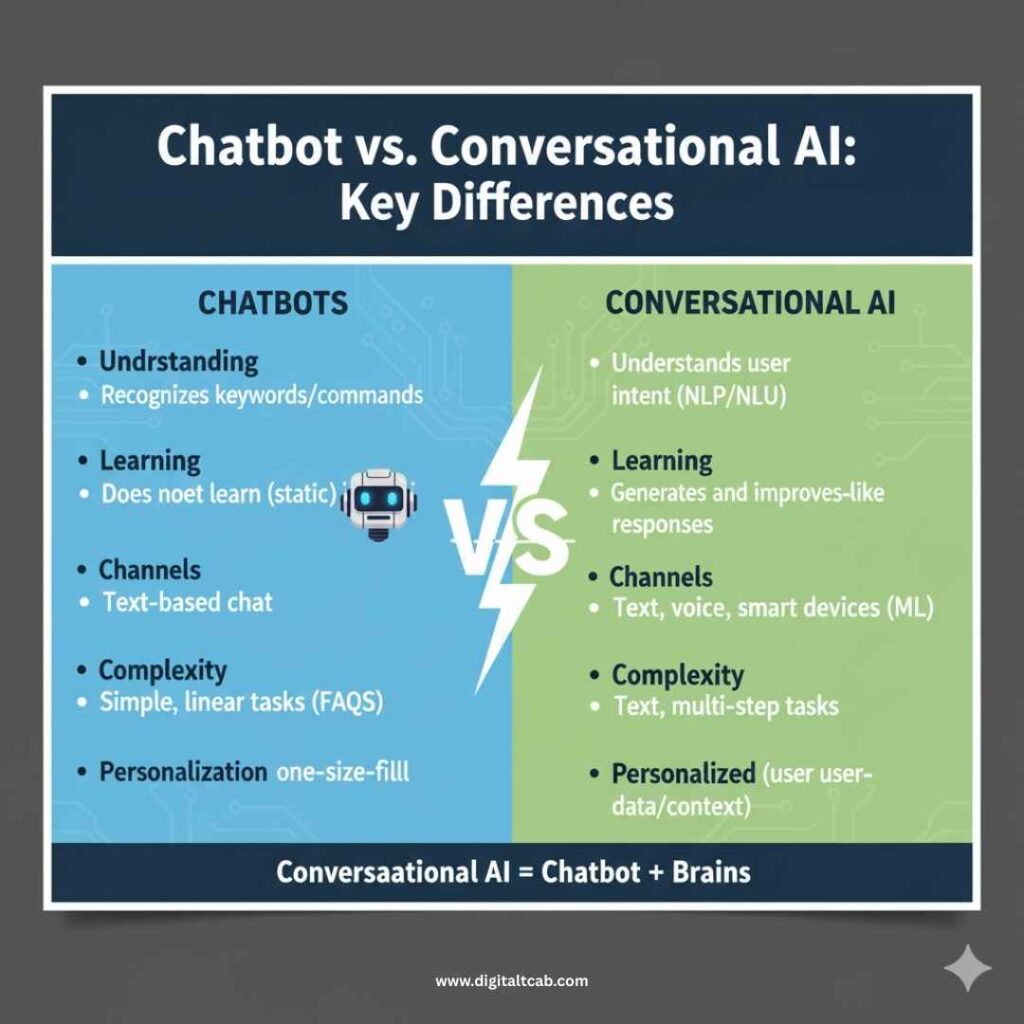
Key Differences Between Chatbots and Conversational AI
The key difference between a chatbot and conversational AI lies in sophistication: chatbots follow predefined scripts, whereas conversational AI systems understand context and learn over time. Not all chatbots are powered by AI, but all conversational AI solutions can be considered chatbots with advanced capabilities.
Here’s a quick comparison of chatbots vs. conversational AI:
- Understanding: Chatbots recognize specific keywords or commands. Conversational AI understands the intent behind your words (thanks to NLP/NLU), so it grasps meaning even if you phrase things differently.
- Learning: Chatbots do not learn from interactions – they’re as smart as their initial programming. Conversational AI learns and improves with each conversation (using machine learning).
- Channels: Chatbots are often limited to text-based chats on a website or app. Conversational AI can span multiple channels – text, voice, smart devices – and provide a unified experience.
- Complexity of Tasks: Chatbots handle simple, linear tasks and FAQs. Conversational AI can manage complex, multi-step tasks (like troubleshooting a product or making a reservation with follow-up questions).
- Personalization: Chatbots give one-size-fits-all responses. Conversational AI can personalize responses based on user data and context (e.g. greeting you by name, recalling past questions).
Think of it this way: a basic chatbot is like a flip phone with a few preset functions, while conversational AI is like a smartphone that can run apps and adapt to your needs. Both can make a call (or answer a query), but one is far more capable and flexible.
It’s no surprise that conversational AI offers a better user experience. Conversations with an AI feel more natural and can handle ambiguity. If you deviate from the script with a simple bot, it’s lost. A good AI bot, on the other hand, can adjust – “Oh, you meant X? Here’s the answer.” (When you hear someone complain that a chatbot was “dumb”, it’s usually because it was a rigid rule-based bot with no conversational AI.)
Gartner predicts that by 2027, roughly 25% of organizations will use chatbots as their primary customer service channel. That indicates a significant shift toward automation – and to meet that expectation, many of those bots will need conversational AI capabilities. After all, friendly, efficient self-service can boost customer satisfaction, but only if the bot is smart enough to be truly helpful.
When to Use Chatbots vs. Conversational AI (Complexity, Budget, etc.)
Use simple chatbots for basic, frequent tasks, and opt for conversational AI for complex or high-volume interactions that require a more nuanced understanding and response.
In practice, here are some guidelines:
- Scope & Complexity: If you only need to answer straightforward FAQs or handle simple tasks (such as adjusting store hours or tracking an order), a rule-based chatbot may be sufficient. However, if users expect to ask anything (even vague or multipart questions) and receive a helpful answer, a conversational AI solution will perform better.
- Budget & Resources: Chatbots are typically cheaper and faster to implement – there are even no-code bot builders available. Conversational AI requires a bigger investment in technology and expertise (for NLP training, integration, etc.), but it pays off by handling more complex tasks and improving over time. Consider a chatbot as the budget-friendly starting point, and conversational AI as the premium upgrade.
- User Expectations: If your audience needs quick answers to widespread questions, a basic chatbot keeps things efficient. However, if they expect a personalized, human-like interaction – such as a fintech app for tech-savvy users or a healthcare service handling sensitive information – a conversational AI is more likely to meet (and exceed) those expectations.
- Scalability: For a high volume of diverse queries, an AI-powered bot that can learn and adapt is far more scalable (it won’t break a sweat even if questions vary widely). If you only receive a small volume of repetitive queries, a simpler bot is often enough. As your query complexity and volume increase, the case for conversational AI grows too.
Many businesses actually start with a simple chatbot for quick wins, then upgrade to conversational AI as their needs (and budgets) expand. That can be an innovative approach: you get immediate automation for FAQs, and you learn from that experience to inform a more advanced AI deployment later.
Industry Examples: Chatbots and Conversational AI in Action
Let’s explore how different industries leverage these tools:
- E-commerce & Retail: Retailers use chatbots to assist shoppers and boost sales. For example, Domino’s Pizza has a chatbot named “Dom” on Facebook Messenger that allows customers to place orders via chatdevrev.ai. Other online stores utilize chatbots to recommend products and address questions about stock or shipping, which helps reduce cart abandonment. Chatbots in retail can also handle order tracking or simple customer queries (“Where’s my package?”) instantly. The result is a smoother shopping experience – customers get help immediately rather than waiting on hold.
- Healthcare: Healthcare providers use conversational AI to assist patients. For example, some hospitals have virtual assistants to schedule appointments or do basic symptom checks. (During the COVID-19 pandemic, many organizations launched chatbot screeners to help people figure out if they needed testing or emergency care.) This provides patients with quick guidance, freeing up staff to attend to more critical cases. Imagine texting a health bot “I have a sore throat and fever” and getting triage advice in seconds – it’s not a doctor, but it can tell you if you should rest, take meds, or see a physician. Conversational AI in healthcare is also utilized for tasks such as medication reminders and mental health check-ins, always with an emphasis on privacy and accuracy.
- Customer Support: This is one of the biggest domains for these tools. Many banks and telecoms now use bots to handle common questions and troubleshoot issues. For example, the meal-kit brand HelloFresh introduced a chatbot “Freddy” to help answer customer inquiries, and it reduced their response time by 76%. A well-designed support bot works 24/7 and significantly reduces wait times. (One study of large support teams found they saved hundreds of hours per month by using chatbots.) These bots can handle things like billing queries, account balances, or basic tech support (“Did you try restarting the router?”), while more complex issues get escalated to human agents. Customers receive help more quickly, and support agents are less overwhelmed.
Across various industries, companies are discovering innovative ways to utilize chatbots and conversational AI to engage users. We’ve highlighted e-commerce, healthcare, and support. Still, you’ll also see chatbots in finance (banking apps answering questions about transactions), travel (virtual agents that help book flights or provide itinerary updates), and many other fields. The pattern is the same: basic bots cover the simple stuff, while conversational AI handles the complex conversations.
Chatbot Platforms vs. Conversational AI Platforms
One question that often arises is which tools to use for building these bots. Should you go for an easy chatbot platform or a more robust conversational AI platform?
A chatbot platform offers quick, no-code bot building for simple use cases. In contrast, a conversational AI platform provides advanced AI tools (NLP, ML, integrations) for developing cultured, human-like assistants.
- Chatbot Platforms: These are user-friendly services or software for building basic chatbots. They often have drag-and-drop interfaces or templates so that you can set up a rule-based chatbot without programming. They’re ideal for simple workflows or marketing bots. Examples include Chatfuel or ManyChat, which let you create, say, a Facebook Messenger bot to answer FAQs or collect leads in just a few hours. If you have limited technical resources and need a quick chatbot, these platforms are a great starting point.
- Conversational AI Platforms: These are more powerful frameworks designed for building AI-driven bots. They offer advanced capabilities, including natural language understanding, machine learning training, and integration with various channels and databases. Think of tools like Google Dialogflow, IBM Watson Assistant, or Microsoft’s Bot Framework. Using these, developers can create a bot that not only chats, but also understands context, handles speech input/output, and connects to your backend systems. The trade-off is that they require more development effort and expertise. However, if you need a highly customized virtual assistant (for example, a bank’s virtual agent that can pull up transaction history and has secure authentication), a conversational AI platform is the way to go.
In short: Choose a chatbot platform if you want something up quickly for a narrow task, and choose a conversational AI platform if you aim to build a more complex, AI-powered solution that can grow with your needs. Sometimes, businesses start on a chatbot platform and then migrate to a conversational AI platform as they expand features.
Chatbots vs. Virtual Assistants: Impact on Employee Experience
We’ve discussed customer-facing uses, but what about internal applications within a company? This is where the distinction between chatbots and Virtual assistants can significantly enhance the workplace experience.
Chatbots and virtual assistants both automate support, but a virtual assistant (a more advanced conversational AI) acts like a proactive digital coworker. A basic internal chatbot might handle FAQs (“How do I reset my VPN password?”) instantly, saving employees from waiting on IT. Meanwhile, a virtual assistant can function like a personal aide for staff, scheduling meetings, retrieving information from internal systems, or sending reminders — essentially performing tasks on an employee’s behalf.
The result is a better employee experience. Employees can spend less time looking for information and focus more on productive tasks.
For instance, instead of waiting three days for an IT ticket to reset a password, an AI assistant can do it in seconds after a quick identity check. Why waste time searching through an extensive HR handbook when you can ask the bot on your first day? These tools also reduce repetitive tasks for HR and IT teams, allowing them to focus on more critical projects.
Employees feel more supported, and the business saves resources — it’s a win-win.
For instance, I saw one company deploy an AI assistant in their office chat (Slack). Employees would ask for things like policy forms or scheduling a meeting, and the assistant would instantly provide the info or propose a time. It cut down tons of back-and-forth emails, and employees absolutely loved it. Unlike basic bots, a virtual assistant can even proactively nudge employees (“Reminder: you have 5 PTO days left this year!” or “Great job on that Q3 sales target – here are the next steps.”). A simple chatbot would never do that, because it lacks context and initiative.
For organizations evaluating AI-powered solutions for conversational AI chatbots versus assistants to enhance employee experience, the key is to start with what brings value quickly and then scale up. In summary, for internal use:
- Internal Chatbots: Focus on answering common employee questions and providing quick self-service for basic needs (HR policies, IT help, etc.).
- AI Virtual Assistants: Integrate with workplace systems and handle more complex, multi-step tasks (like onboarding workflows, expense report filing) or proactive alerts.
Many businesses begin with a chatbot for internal support and gradually evolve it into a more capable AI assistant as their needs grow and the AI learns from interactions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Are chatbots and conversational AI the same thing?
Not exactly. A chatbot is a software program for chatting with users (it can be simple or fairly advanced). In contrast, conversational AI refers to the intelligent technology that enables more natural, human-like conversations. In other words, conversational AI powers the most advanced chatbots. A basic rule-based chatbot isn’t using true AI – it’s following a script – while an AI chatbot uses conversational AI to understand and respond more flexibly.
Which is better for customer service, a chatbot or conversational AI?
It depends on your needs. For straightforward questions and simple issues, a regular chatbot works well and provides instant answers. For more complex or sensitive inquiries (where understanding context or nuance is essential), a conversational AI will deliver a superior experience. In fact, many businesses use both: the chatbot handles common, FAQ-type questions, and if something is too complex, it refers the issue to an AI assistant or a human agent. This blended approach offers customers the advantages of both options.
What are some good platforms for chatbots and conversational AI?
For chatbot platforms, user-friendly options include Chatfuel or ManyChat, which let you build simple bots quickly without coding. For conversational AI platforms, consider tools like Google Dialogflow or IBM Watson Assistant, which offer advanced AI capabilities (language understanding, integrations, etc.) to build more complex, scalable assistants. The choice depends on your project – opt for chatbot platforms for quick and simple bots, and AI platforms for power and flexibility.
Will chatbots or conversational AI replace human agents?
No, not completely. Chatbots and AI assistants are great at handling routine questions and tasks, but there will always be complex issues or personalized care that only humans can provide. In practice, the best strategy is to let AI handle the simple stuff and seamlessly hand off more complicated matters to human agents. This way, your human team can focus on high-value interactions while bots handle the repetitive FAQs. Rather than replacing humans, AI often works alongside them to increase overall efficiency.
Can these chatbots work in multiple languages?
Yes. Many AI chatbots are capable of understanding and replying in multiple languages, thanks to NLP. You can train or configure them for different languages. Rule-based bots can be set up in other languages as well, but a conversational AI with strong language processing can even detect a user’s language and adjust responses accordingly. This makes chatbots and AI assistants handy for global or multilingual audiences.
Conclusion
As AI technology evolves, the distinction between basic chatbots and advanced conversational AI is becoming less clear. However, understanding these differences remains crucial for making the best decision for your needs. The key point is that chatbots are ideal for handling straightforward, repetitive tasks, while conversational AI enables more cultured, natural conversations.
There’s no one-size-fits-all — the right solution depends on your needs, but now you know the key differences and how each can be applied.
Whether you start with a simple bot or dive into a custom AI assistant, the key is to begin. Don’t hesitate to take the next step. Often, it’s best to start with a small pilot project (like a chatbot for one use case), measure its impact, and then iterate or expand. If you found this guide helpful, be sure to explore more insights on our blog. And if you’re looking to implement these solutions, feel free to reach out – I’m happy to help you succeed on your AI journey!


Leave a Reply